Toolbars within the header block of ArcGIS can be updated via the drop menu item (Customize >> Toolbars) or alternatively by right clicking within the header block. Commonly used toolbars for TUFLOW modeling are listed below:
We have designed a toolbar for advanced analyses of your InSAR results in an ArcGIS environment. The toolbar simplifies the process of visualizing data, applying a legend, creating maps (average velocity, cumulative displacement, etc.), displaying time series and analysing motion profiles using the cross-section tool. Jul 17, 2014 Geologic Cross Sections at intera. This feature is not available right now. Please try again later. Visualizing cross sections of lidar data allows you to analyze collections of points from a unique perspective. 2D profile perspectives may make it easier to recognize particular features captured from lidar data, such as surface valleys, mountain peaks, buildings, vegetation types, forest canopy, road corridors, river/stream corridors, mines, construction sites, towers, and even power lines. When you click Create cross section, a separate cross section will be created for each of the selected lines. By default, each new cross section will have a vertical exaggeration of 1, a base elevation of 0, and will display each of the surface layers in the MXD (rasters and TINs) as both a solid and surface. Then navigate to the GeMSTools folder and select file GeMSToolsArc105.tbx (if you are running ArcGIS 10.5) or file GeMSToolsArc10.tbx (if you are running an older version of ArcGIS). Right-click again on empty space in the Arc Toolbox window and select 'Save settings' and then 'Default' to have the GeMS toolbox available next time you open.
- Editor
- Snapping
- Edit Vertices
- ET GeoWizards
- 3D Analyst
- Animation
The Editor toolbar contains a collection of tools to create, update, or delete features directly within the display.
The most commonly used items within the toolbox are:

- Create Feature, used to define what feature types will be created.
- Edit Tool, used to select a feature which already exists for editing.
- Edit Vertices, after selecting a feature using the Edit Tool, this selection will display the vertices of a feature.
- Trace, used to trace existing feature geometry when creating new features. The Layers which are selectable for the tracing can be managed using the selection options via right clicking a layer in the Table of Contents. This is shown in the figure below.
- Sketch Properties, after selecting a feature using the Edit Tool, this selection will display the geometry properties of a feature in tabular format. Values can be updated within the display, modifying the features spatial display.
- Editor>>Stop Editing
- Editor>>Save Edits
Snapping is used to associate point features with lines or polygons. ArcGIS snapping options include: Point Snapping, End Snapping, Vertex Snapping and Edge Snapping. Edge snapping is not recommended for TUFLOW model development tasks. Edge snapping can be disabled by deselecting the Edge Snapping icon in the toolbar. After being deselected, the Snapping toolbar should resemble the figure below.
Items within the edit toolbar are used to modify the location of vertices and add or remove vertices. The Edit and Edit Vertices tools within the Editor Toolbar need to be selected before the Edit Vertices options are selectable
ET GeoWizard is a central location for a wide range of geometry update tools. ET GeoWizard can be downloaded from http://www.ian-ko.com/ET_GeoWizards/gw_demo.htm. The most commonly used items within the toolbox are:
- Polyline >> Split Polyline
- Polyline >> Buffer Polyline
- Polygon >> Eliminate
- Polygon >> Fill Holes
- Convert >> Polygon to Polyline
- Convert >> Polygon to Point
- Convert >> Polyline to Polygon
- Convert >> Polyline to Point
- Convert >> Point to Polyline
- Convert >> Point to Polygon
- Geoprocessing >> Clip
- Geoprocessing >> Batch Clip
- Geoprocessing >> Erase
- Geoprocessing >> Batch Erase
- Geoprocessing >> Merge Layers
- Geoprocessing >> Split by Attribute
- Geoprocessing >> Split by Location
- Geoprocessing >> Transfer Attributes
- Miscellaneous >> Create Station Lines (Water Level Lines)
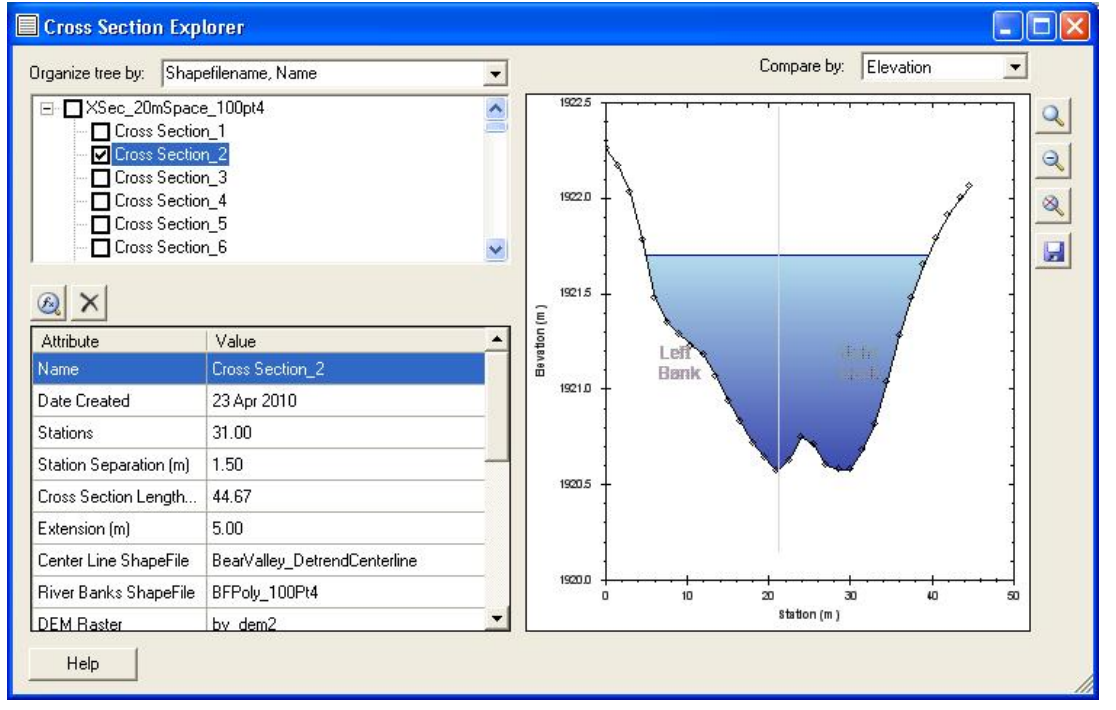
The 3D Analysis toolbar is used to perform analysis tasks on raster datasets. For example, cross-sections can be extracted from 3D raster datasets using the ArcGIS 3D analysis extension. This tool is useful for viewing and extracting creek cross-section or water surface elevation longprofile information.
The steps how to do this are outlined in the following webinar: Webinar Link: Extracting Cross-section Data From Raster
content to be update
| Up |
|---|
You can view geospatial content in Scene Viewer in the portal website.Scene Viewer works with devices that support WebGL, a web technology built into most modern browsers for rendering 3D graphics. You can also author your own scenes when you sign in to Scene Viewer.
Note:
Before you open Scene Viewer, verify that your browser supports scenes.
Navigate your scene
Navigate scenes with Scene Viewer tools or use your mouse or touch device to move around scenes.
Tools
You can move around scenes with the following Scene Viewer tools:
- Click Initial view to return to the initial camera position.
- Click + to zoom in.
- Click - to zoom out.
- You can also use your mouse and scroll wheel to zoom in and zoom out, or click and hold the wheel button and move down or up to zoom in or out.
- Click Pan to pan. Click and hold the mouse button and drag the scene in the direction you want to move it. You can also pan using the arrow keys on the keyboard.
- Click Rotate to rotate. Click and hold the mouse button and drag the scene in the direction you want to rotate and tilt it.
Note:
When you click either tool, the mouse button becomes the primary navigation and the right mouse button the secondary navigation. For example, click Rotate to use the mouse button to rotate and the right mouse button to pan. The black triangle at the upper right of the tool indicates the tool is selected.
- Compass shows the orientation of the scene. Click Compass to set your scene to North orientation.
Devices
The following navigation methods can be used with devices:
- Scene Viewer provides viewing experiences for smartphones and tablets. With smartphones, you can navigate your scene with a simplified viewing experience without authoring or tools. Tablets offer the same UI as desktop computers.
- If you have touch capabilities on your device, you can pinch zoom with two fingers and pan with one finger. You can also double-tap the scene to zoom in a step toward the tapped location. To rotate the scene, move two fingers in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. To tilt the scene, drag two fingers up or down the screen.
Note:
The Pan/Rotate switch navigation controls and 3D Navigation settings do not affect touch.
- Scene Viewer supports standard gamepads and 3Dconnexion SpaceMouse devices for intuitive navigation. See Scene Viewer navigation devices for more information.
Actions
The following are helpful navigation actions you can use:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
Double-click | Zoom in at pointer. |
Press Arrow keys | Move the view left, right, up, or down (global scene only). |
Press B+Left click | View from the current camera position. |
Press A | Rotate view counterclockwise. |
Press D | Rotate view clockwise. |
Press W | Tilt camera up. |
Press S | Tilt camera down. |
Press J | Move down, closer to the view (global scene only). |
Press U | Move up, away from the view (global scene only). |
Press P | Set your scene perpendicular to the ground. |
Press N | Set your scene to North orientation. |
Press Ctrl+S | Save your scene. |
Press Ctrl+E | Start and stop sun animation over a day period. |
Drag with one or multiple fingers | Pan. |
Double-tap with one finger | Zoom in at the finger position. |
Use two fingers to pinch in or out | Zoom in or out. |
Move two fingers in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction | Rotate. |
Drag two fingers up or down the screen | Tilt the scene. |
Explore building scene layers
The Building explorer tool allows you to explore building scene layers that contain the fine details of buildings such as walls, lighting fixtures, and mechanical systems. When your scene contains building scene layers, the Building explorer tool is added at the bottom of the Scene Viewer tools.

Building scene layers can contain complex digital models of buildings and interiors and allow you to interact with all the components of the building through multiple layers. Often, they contain an overview layer that serves as an exterior shell and helps you view the building model as a single feature. Building scene layers are organized under the Disciplines & Categories heading. Discipline layers are group layers that organize the building scene layer content into architectural, structural, mechanical, or electrical groups when available. These group layers contain a number of Category layers such as walls, windows, furniture, and lighting fixtures.
Display building scene layer
To explore building scene layers, do the following:
- Click the Building explorer tool .
- Select the building scene layer you want to explore from the drop-down menu.
The building scene layer expands and allows you to see all the layers under the Disciplines & Categories heading.
- Click a building scene layer element, such as a door or wall, to display a pop-up about the feature.
- Click the layer and sublayer check boxes to show and hide features in the scene.
- To explore another building scene layer, select a new layer from the drop-down menu or click a different building scene layer in your scene.
- The state of the layer visibility settings for each building scene layer is preserved in the Building explorer tool.
- When you select a different building scene layer, the scene zooms to the building scene layer and expands the layers in the tool.
- Click None to collapse the layers in the tool and display only the overview layer in the scene.
- The state of the layer visibility settings is preserved in the Building explorer tool.
- When a building scene layer doesn't have an overview layer, the layers collapse in the tool and the building scene layer remains the same in the scene.
You can explore only one building scene layer at a time using the Building explorer tool.
Alternatively click different building scene layers in your scene to explore with the Building explorer tool.
- When the building scene layer has an overview layer, the Building explorer tool opens.
- When an overview layer isn't present, a pop-up appears containing information about the highlighted element without opening the Building explorer tool.
Isolate a level
You can isolate a level of a building scene layer using the Level picker in the Building explorer tool. When you choose the level, the levels below become semi-transparent for added visual context.
Choose construction phase
When construction phases are available in the building scene layer, under the Construction phases option, you can choose a numbered phase to display. The building scene layer includes information indicating the phase the components were created, and optionally, when they were removed.
Click a construction phase to display all the components created during or before the phase. Removed components aren't displayed.
Apply filter
When predefined filters are present, the Building explorer tool displays the Filter button , indicating that predefined filters were previously configured in the scene, such as from ArcGIS Pro 2.4 or later.
To filter a building scene layer, do the following:
Arcgis Cross Section Tool Set
- Click the Filter button .
- Select a predefined filter.
- The scene displays the components configured in the predefined filter.
- The layer settings under the Disciplines & Categories heading no longer appear.
- Click the Filter button again and select No predefined filter to remove the filter and display the Disciplines & Categories layer settings.
Caution:
The Building explorer tool layer settings under Disciplines & Categories override the predefined filters. To ensure that the predefined filters display, verify that the corresponding layers are checked under Disciplines & Categories.
Slice scene content
Aspect Tool Arcgis
You can use the Slice tool to reveal occluded content in a scene. The Slice tool hides any layers or terrain the slice intersects. For example, you can slice a building to display inside layers, such as interior walls and furniture.
Create a slice
To create a slice, do the following:
- Click Analyze to access the Slice tool .
- Click the Slice tool .
- Click New Slice.
- The tool indicates where the scene will be sliced.
- Press Ctrl/Cmd or Shift while clicking to slice with either a horizontal or vertical plane, respectively.
- Click a surface or object to make a slice.
The slice hides any content in front of the surface.
- Drag the handles of the slice plane to move, resize, or rotate the slice.
- Click New Slice again to start a new slice.
- Close Analyze to hide the slice.
- Click the Slice tool again for the slice to reappear in the scene.
Exclude layers
After a slice is created, you can exclude layers from the slice. For example, you can set the HVAC and windows layers in a building to remain visible while you slice.
- Click Exclude Layer from Slice.
- Click a layer in the scene to exclude from the slice.
The layer is added to the Excluded layers list.
- Click Cancel to return to the initial view.
- Click Exclude Layer from Slice again to make another layer visible.
- Click the Remove button next to the layer name to remove it from the Excluded layers list.
Interact with a slice
Once you've created a slice, you can explore and examine your scene further with Scene Viewer tools, such as Pop-ups and Measure. For example, you can measure the length of an HVAC air duct inside a building that was previously hidden.
Measure scene
The Measure tools allow you to measure distances between two points and calculate areas in your scene. When you click the Measure distance tool or Measure area tool , horizontal laser lines are projected on the terrain and any objects in the scene. This visually shows the vertical height of the pointer as you measure. It is helpful to see the heights of objects relative to other objects and the terrain. For example, you can hover over a smaller building and see that height highlighted relative to another part of the terrain.
Distance
Use Measure distance to calculate the distance between two points in a scene. The Measure distance tool labels the direct, horizontal, and vertical distance lines in the scene and displays the values in the panel.
- Direct—Distance between two points
- Horizontal—Horizontal distance between two points
- Vertical—Vertical distance between two points
While you are measuring, a second laser line indicates where the vertical plane along the checkered line intersects the terrain in all directions, such as with buildings, bridges, and the ground.
To measure distance, do the following:
- Click Analyze to open the Measure tools.
- Click Measure distance .
- Click in the scene to start measuring.
- Click to set the endpoint.
- Click New Measuement to start a new measurement.
When the distance between the points is greater than 100 kilometers, a circular laser line appears indicating that Scene Viewer has switched to geodesic mode. In geodesic mode, Scene Viewer only calculates the horizontal and vertical distances, taking into consideration the curvature of the earth (that is, ellipsoid-based geodesic distance). The Direct distance option is unavailable.
Area
Use Measure area to calculate the area of a polygon you draw. While measuring, the Measure area tool labels the current segment length and the total length of the path in your scene. Once you close the path, a polygon is created with labeled values for the area and perimeter. These values also appear in the panel.
- Area—The area of the polygon
- Perimeter—The perimeter length of the polygon
To measure area, do the following:
- Click Measure area .
- Click in the scene to start adding points to the polygon.
- Double-click to close the path and calculate the polygon area. Alternatively, click the starting point again to close the path.
- Click New Measuement to start a new measurement.
When the polygon perimeter is greater than 100 kilometers, Scene Viewer switches to geodesic mode. In geodesic mode, Scene Viewer calculates the values, taking into consideration the curvature of the earth (that is, ellipsoid-based geodesic values).
After measuring
To adjust either the Measure distance or Measure area measurement, hover over any point and drag. As you drag points, Scene Viewer displays the adjusted values in the scene and panel. You can change the unit of measure under Unit.
Note:
In local scenes, measurements are displayed as Euclidean values and may not be accurate depending on the scene's projected coordinate system. Web Mercator scenes display the accurate geodesic values.
Search
You can search for locations, such as addresses or places. Click Search and type a keyword in the search box. Click a result in the list or press Enter to navigate to that location. You can also configure search to search for specific features in layers, such as points of interest or building names.
View layers
Use Layers to manage the visibility of layers in your scene. Click the check boxes to turn layers on and off in the scene. You have the following options:
- Click Layers to view the layers of the scene.
- Click the Zoom to button to zoom your scene to the layer's extent.
- Click Legend to see the symbology of the layers.
- Click Layers again or another tool to close.
Choose a basemap
Click Basemap to switch your basemap and set ground transparency for the scene.
Adjust daylight
Open Daylight to change how sunlight and shadows affect your scene during different times of the day and year.
Sunlight slider
Drag the Sunlight slider left and right to adjust the sunlight and shadows in your scene at different times of the day. You can also adjust the time of day by manually entering it or by clicking specific times on the slider. To change time zones, click the current time zone to the right of the time box and choose from the drop-down list.
Click Play to animate the sunlight as it cycles through the day in your scene.
Calendar
Click the Calendar drop-down menu to change the sun's position at different times of the year.
Click Play to animate the sunlight as it cycles through the months in a year in your scene.
Shadows
Check Show shadows to illustrate shadows in your scene. You can change shadow effects by adjusting the Sunlight slider , time zone, and Calendar options.
Share the scene
Click Share to share the scene by email or social media, embed it in a website, or create a web app from the scene.
Change settings
Settings contains tools you can use to adjust performance quality and mouse navigation settings for your browser.
Performance and quality
Choose from the following settings to optimize 3D graphics rendering:
- Quality—Use higher-quality visualization options, such as realistic atmosphere.
- Balanced—Set equal optimization of performance and quality.
- Performance—Increase stability and speed by reducing data load.
3D navigation
For 3D Navigation, choose either the default Scene Viewer navigation or the ArcGIS Pro mouse navigation.
Display the scene in full screen
Click Full Screen at the lower right to switch to full screen mode. Exit full screen mode by clicking Exit Full Screen (Esc) or pressing Esc on your keyboard.
